Course: Speech Coding, Summer Term 2013
Please visit the education page for information on current courses.
Lecturer
Prof. Dr. Tom Bäckström
Guest Lectures
Guillaume Fuchs, Jeremie Lecomte, Christian Uhle
Time
Summer Term 2013, Thu 14.15-16.00
Place
Am Wolfsmantel 33, Erlangen-Tennenlohe, Room 3R4.04
Registration
Please come to the first lecture on Thursday, 19.04.2013, 14:15 - 15:45, Room 3R4.04 (Tennenlohe). If you are unable to attend, please contact Prof. Dr. Tom Bäckström.
Content
Mobile phones – everyone has one. With 7 billion mobile phones in use, digital speech transmission is a truly global technology. Your grandma has one, Prince Charles has one and the poorest village in Africa has one. While the technology clearly works already, with such a market, the smallest improvement, when multiplied by 7 billion, has a huge impact worldwide.
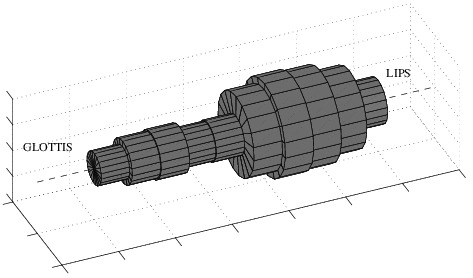
Speech coding refers to digital compression and transmission of speech. This course provides an in-depth perspective to ACELP, the most commonly used speech coding algorithm. We will study the speech production models on which it is based, the perceptual models which are used for its optimization, and most importantly, go through the theory and practice of the most important concepts, linear prediction (LP), long time prediction (LTP), algebraic codebooks, line spectral frequencies (LSFs) and windowing. In addition, we will look at the big picture, the additional challenges that emerge when building a commercial speech coding product.
The goal of this course is to provide a strong foundation for researchers, engineers, and graduate students who are interested in the problem of speech coding.
Tentative Schedule
- 18.4 -- Introduction & Speech Production and Perception (handouts: introduction, motivation & production)
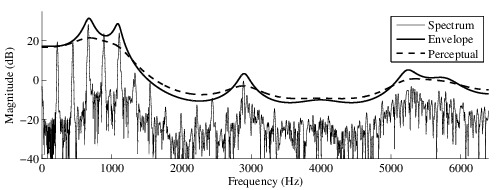
- 25.4 -- Envelope and Masking (handouts: envelope, chapter: envelope)
- 2.5 -- Envelope (continued)
- 9.5 -- bank holiday, no lecture
- 16.5 -- Windowing and Fundamental Frequency (handouts: windowing, fundamental frequency, chapters: windowing, fundamental frequency)
- 23.5 -- Residual Modelling, Algebraic Codebooks (handouts: residual, algebraic, chapters: residual)
- 30.5 -- bank holiday, no lecture
- 6.6 -- cancelled
- 13.6 -- Residual (continued) and Gain Coding (handouts: gains, chapter: gains)
- 20.6 -- Packet Loss (handouts: packet loss)
- 27.6 -- Relaxed Modelling (RCELP) (chapter: RCELP)
- 4.7 -- Voice Activity Detection (handout: VAD)
- 11.7 -- Quality Evaluation (handout&chapter: quality)
- 18.7 -- Systems Design, Fixed Point Implementation and Complexity (handouts: resource allocation and systems design)
Course requirements
This course is the most advanced course offered by the university on this topic, and serves as an excellent basis from which to commence research in the area. Various aspects of the course bring students up to date with the very latest developments in the field, as seen in recent international standards, conferences and journals. This course builds on Sprach- und Audiosignalverarbeitung (by Prof. Kellermann), and is well complimented by Mensch-Maschine-Schnittstelle (by Prof. Rabenstein), Praxis der Audiodatenkompression (Dr. Grill), Speech Enhancement (Prof. Habets) and Selected Topics in Perceptual Audio Coding (Prof. Herre), which deal with many other signal processing methods and gives an understanding of human auditory perception (also a key part of speech coding) and audio compression techniques.
Course material
If your are missing handouts or chapter printouts, please contact the lecturer (tom.backstrom@audiolabs-erlangen.de) or Johannes Fischer (johannes.fischer@audiolabs-erlangen.de).